The Environmental Defense Fund wrote the cap-and-trade approach to sulfur emissions into the 1990 Clean Air Act. A similar program has become law in California to limit carbon emissions, where implementation will begin in 2013. The cap part of the program is an incrementally rising cap on the legally allowable limits for carbon emissions factories produce. The trade portion allows companies that reduce their emissions to a lower level than the legal mandate to use the difference as a credit that a company exceeding the legal limit can buy to bring itself into the compliant range of emissions output.
The EDF explains the history of cap-and-trade, which started in 1990
Traditional, top-down government regulation would have simply directed every plant owner to cut pollution by a specific amount in a specific way. But this method, critics said, would cost too much, impede innovation and ignore the knowledge and initiative of local plant operators.
The way forward, EDF experts argued, was to harness the power of the marketplace. Our cap-and-trade approach, written into the 1990 Clean Air Act, required that overall sulfur emissions be cut in half, but let each company decide how to do it. And power plants that cut their pollution more than required could sell those extra allowances. A new commodities market was born.
Under this market-based plan, sulfur emissions have gone down faster than predicted and at one-fourth of the projected cost. By 2000, scientists were documenting decreased sulfates in Adirondack lakes, improved visibility in national parks and widespread benefits to human health. The Economist called it “the greatest green success story of the past decade.”
EDF explains that the California cap-and-trade market for greenhouse gases addresses is modeled after their plan.
In October 2011, the California Air Resources Board voted to create a cap-and-trade market for greenhouse gases, as required by AB32, the state’s landmark bipartisan 2006 climate bill, which EDF cosponsored and defended in court.
AB32 aims to cut greenhouse gas emissions in California, the world’s eighth largest economy, to 1990 levels by 2020, while generating one-third of its electricity from renewable sources like solar and wind.
The cap-and-trade market alone, which begins operating in 2013, will slash the state’s warming emissions by an amount equivalent to taking some 3.6 million cars off the road.
The LA Times reports
Environmental justice groups oppose aspects of the program, arguing that cap-and-trade’s market allows refineries, power plants and other large-scale facilities to continue polluting poor neighborhoods as long as they purchase credits or offsets ..
and gives details about how the carbon cap-and-trade program will work in California
Emissions caps were established by collecting three years of emissions data from the state’s largest industries. Those businesses were grouped into sectors and assigned an average emissions benchmark. Businesses are allowed to emit up to 90% of that amount in the first year. Companies that operate efficiently under the cap may sell their excess carbon allowance on the market; companies whose emissions are above the benchmark must either reduce their carbon output or purchase credits or offsets.
Offsets are a way of turning carbon “savings” into tradable equities. For instance, a forestry company may change its practices so that its forests store more carbon. That increase in carbon storage can be turned into a marketable credit. An independent entity would verify that the carbon savings are real. That additional storage must be maintained for at least 100 years. No carbon offsets may be purchased from non-U.S. sources.
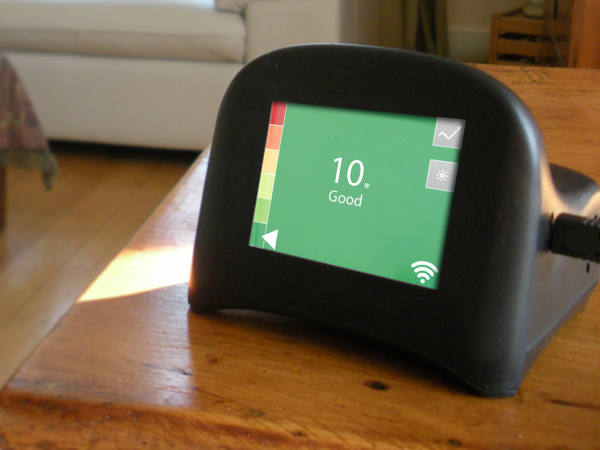 NPR reports on a groundbreaking Pittsburgh library innovation: the Carnegie Mellon Library is lending out the Speck air quality monitor (cost $200) to help residents stay healthy.
NPR reports on a groundbreaking Pittsburgh library innovation: the Carnegie Mellon Library is lending out the Speck air quality monitor (cost $200) to help residents stay healthy.